Embedded Insurance: A Paradigm Shift in Coverage Delivery
Published on 02 Jan, 2025

Embedded insurance integrates insurance into transactions such as purchasing a car, booking travel, and using digital services. Offered at the point of sale, it simplifies traditional processes, enabling instant and effortless coverage. Examples include trip cancellation insurance on travel platforms, ride-hailing apps bundling accident insurance, and e-commerce sites offering extended warranties. Embedded insurance enhances convenience, broadens insurer reach, and caters to modern consumer demands for personalized, flexible solutions. While challenges like regulatory complexities and data privacy exist, technological advancements and strategic partnerships drive innovation, making embedded insurance a transformative, accessible, and integral part of future marketplaces.
Understanding Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance is a delivery model that integrates insurance into everyday transactions. Whether buying a car, booking a vacation, or subscribing to a digital service, insurance is offered directly at the point of sale or use. This streamlined approach removes the complexity associated with traditional processes, allowing customers to secure protection effortlessly—either as an automatic inclusion or an optional add-on, without lengthy applications or comparisons.
Travel platforms including trip cancellation coverage during booking; ride-hailing apps bundling personal accident insurance with rides; and e-commerce sites offering insurance and extended warranties at checkout are a few common examples of embedded insurance.
This approach enhances customers' convenience while enabling insurers to expand their reach, particularly into underserved markets. Few companies adopted embedded insurance to enhance customer experience. Volvo offers 3-year comprehensive insurance bundled with the purchase of select electric vehicle models in Germany through Allianz, its insurance partner. Also, Alterra Mountain Company, an adventure sports management company, offers injury insurance with its Ikon Pass—a pass offering access to various skiing destinations—through its insurance partner, Spot Insurance.
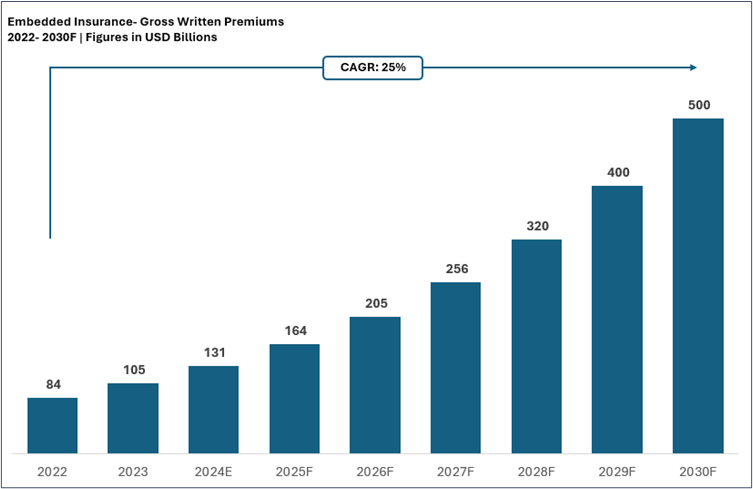
The market for embedded insurance is expected to grow exponentially to reach USD 500 Bn by 2030, owing to rising consumer demand for convenience, technological advancements, and collaborations between insurers and non-insurance businesses.
Digital platforms and data analytics enable personalized and real-time offerings, providing consumers with seamless and cost-effective coverage at the point of sale. Additionally, increased awareness and the shift to online transactions are further accelerating the market, making insurance more accessible and integrated into daily purchases.
Embedded Insurance is Expected to Transform the Industry
Streamlining the Customer Journey - Embedded insurance eliminates the friction of traditional purchasing methods by integrating coverage into existing transactions.
For customers:
- Minimum effort: Insurance becomes part of their familiar buying experiences.
- Instant activation: Coverage begins immediately, offering peace of mind.
For insurers: Embedded models attract customers who may not have actively sought insurance, improving accessibility and acquisition.
- Catering to Evolving Expectations: Modern consumers demand digital-first, personalized, and flexible solutions, which embedded insurance delivers.
- Personalization: Using data analytics, insurers tailor policies to specific needs, like offering trip coverage for frequent travellers or pay-as-you-go auto policies for occasional drivers.
- Flexibility: Short-term and usage-based models align with dynamic consumer lifestyles.
By meeting these preferences, embedded insurance fosters trust and satisfaction.
Expanding Across Industries - Originally dominant in travel and e-commerce, embedded insurance is now reshaping various sectors:
- Healthcare: Wearable devices and telehealth platforms integrate health insurance into subscription services, using real-time data for tailored coverage.
For instance, Humana, a US-based health insurance company, has partnered with Fitbit, a wearable device manufacturer, to use data from Fitbit Care, a wearables platform by Fitbit, to provide customized health insurance to Fitbit users.
- Mobility: Automakers and car-sharing services embed insurance with purchases or rentals, simplifying protection.
- Retail: Electronics and other high-value products often include optional or built-in warranties.
This sectoral expansion highlights the versatility of embedded insurance and its significance in interconnected ecosystems.
Fostering Strategic Partnerships - Partnerships drive the success of embedded insurance, creating mutual benefits for insurers and businesses based on the B2B2C model. These collaborations reduce distribution costs and improve scalability for insurers while businesses benefit from enhanced customer value.
For instance, fintech platforms embed insurance into their services, such as offering income protection with loans. Companies like Uber, Airbnb, and Amazon also use embedded insurance to enhance their offerings and boost customer loyalty.
Paving the Way for a New Industry Standard - Embedded insurance is poised to become a defining feature of the industry. Embedded models address underinsured segments in emerging markets, filling critical gaps in insurance adoption. Further, as embedded options become ubiquitous, customers expect insurance to be integrated into their purchases.
Regulations Concerning the Embedded Insurance Industry – Currently, embedded insurance operates without dedicated regulatory bodies; however, it requires compliance with the regulations governing the industries in which it functions. Key areas of compliance include:
- Licensing: A valid insurance license is essential for offering embedded insurance. Businesses selling insurance directly on their platforms must obtain licenses from national regulators. Alternatively, collaborating with licensed third-party insurers allows businesses to integrate insurance into their offerings without navigating the complexities of licensing.
- Advertising: The ability to market embedded insurance depends on the licensing status. Unlicensed businesses are restricted from promoting insurance features, which may constitute selling or negotiating insurance. In contrast, licensed third-party insurers can advertise insurance products freely, provided they comply with the applicable regulations.
- Data Protection: Embedded insurance requires sharing consumer data between businesses and insurers, making compliance with data privacy, transparency, cybersecurity, and consumer protection laws essential. Companies must also adhere to evolving regulations governing AI to ensure lawful and ethical practices.
InsurTech Firms, a key enabler, cash on opportunities
The anticipated rise in the adoption of embedded insurance creates significant opportunities for IT services providers and InsurTech firms that facilitate the seamless integration and delivery of embedded insurance. As the market expands, these firms are expected to evolve and innovate to develop technology solutions that streamline and enable easy integration of embedded insurance products for a range of end users. Few companies that are leading the charge to normalize embedded insurance include:
- Bolttech, a Singapore-based InsurTech company, provides a digital insurance platform integrating insurance offerings with product or service purchases. The company serves clients across various industries, including financial services, retail, telecom, consumer electronics, travel, and healthcare. Notable clients include LG U+, Samsung, T-Mobile, and Orange.
- Cover Genius, an InsurTech platform, offers embedded insurance via its distribution platform, XCover. It caters to retail, mobility and auto, gig economy, bank/neobank, and payments/fintech, among other segments. Its clientele includes Amazon, Uber, Ryanair, Turkish Airlines, and ShipRush.
- Qover offers tailored embedded insurance solutions to meet the specific insurance needs of businesses and consumers. It caters to major industries, including travel, mobility, e-commerce, and others. It has also partnered with leading brands such as Canyon, Deliveroo, and Revolut.
- Tigerlab, another InsurTech company, offers insurance platform, embedded insurance, and digitalization services. The company provides embedded insurance for jewellery and watches, hearing aids, tickets and events, gadgets and electronics, and bikes and scooters at the point of purchase. Its clientele comprises Magento, Shopify, WooCommerce, 1NOW, and Brown & Neuwirth.
Challenges in Embedded Insurance
While embedded insurance offers immense potential, it also presents challenges:
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating varying regulations across regions is difficult for global platforms.
- Data Privacy: To maintain trust, sharing consumer data between insurers and partners requires robust security.
- Awareness: Educating customers about embedded policies is essential to avoid confusion or dissatisfaction during claims.
Despite these hurdles, technological advances and increasing demand for convenience drive innovation.
The Road Ahead for Embedded Insurance
- IoT Integration: Smart devices will enable real-time, personalized coverage adjustments, such as for auto insurance based on driving behaviour and home insurance based on home automation sensors, among others.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Embedded policies can promote eco-friendly behaviours, like incentivizing the use of electric vehicles.
- Automation: Advancements in digital technologies, including Artificial Intelligence, among others. These developments will aid in streamlining policy issuance, claims processing, and customer support, enhancing efficiency and experience.
Way forward
More than just convenience, embedded insurance represents a paradigm shift in delivering coverage. It is setting a new benchmark for the industry by aligning with consumer habits, using advanced technology, and fostering collaborative ecosystems. As this model becomes increasingly integrated into digital and physical marketplaces, it promises to make insurance more accessible, relevant, and effortless, shaping the future of the insurance landscape.
