Gravity Batteries: Stacking the Future of Energy Storage
Published on 03 Feb, 2025
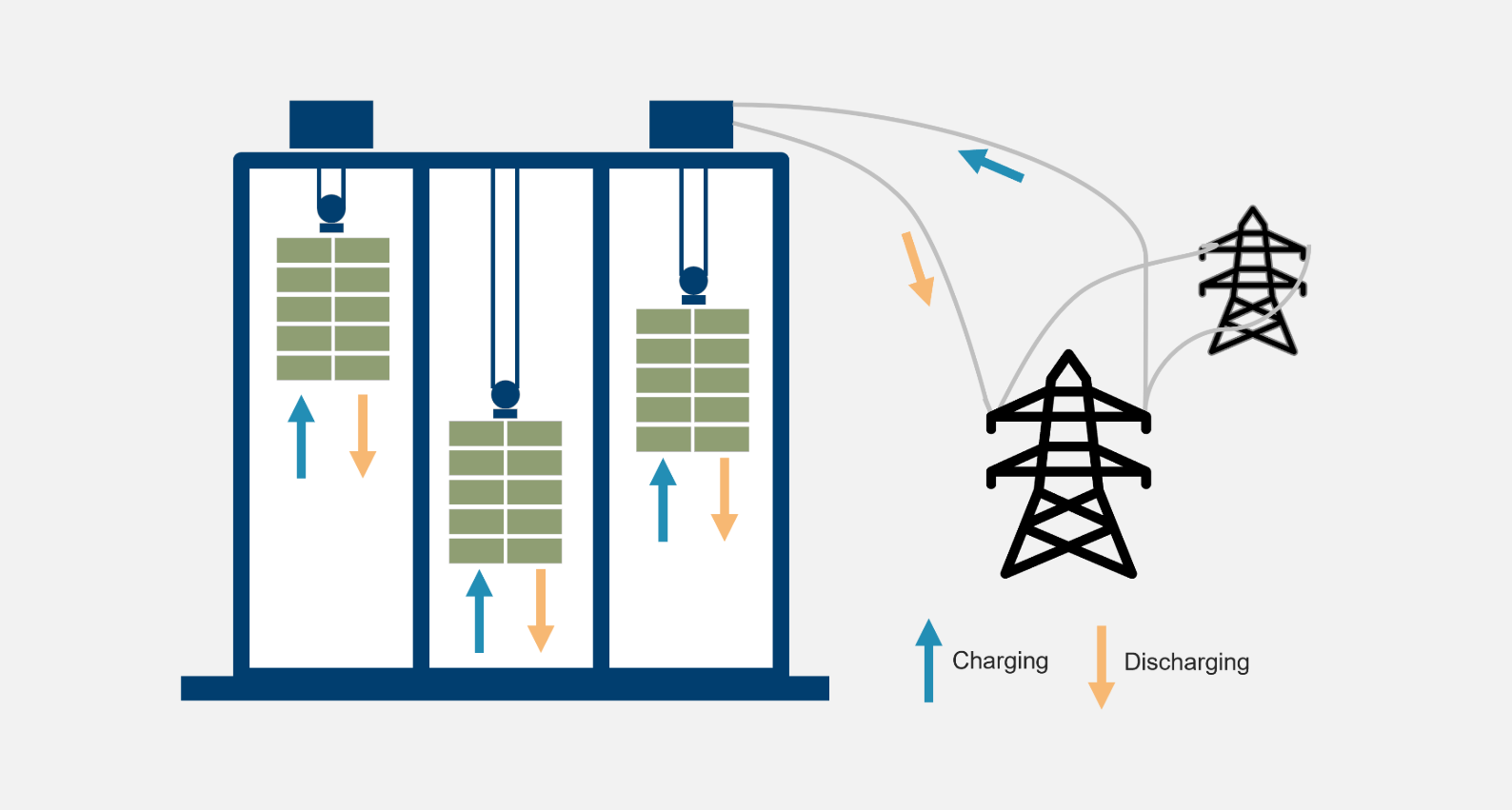
Gravity energy storage, or gravity batteries, is an emerging technology that utilizes gravitational potential energy for large-scale, sustainable energy storage. This system operates by lifting a heavy mass using energy and later releasing it to produce electricity through a generator. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which degrade over time and pose environmental challenges, gravity-based storage offers a durable and eco-friendly alternative. As the demand for cleaner energy solutions grows, innovators are exploring gravity-driven systems as a promising option for efficient and long-term energy storage.
The idea of gravitational energy storage is not entirely new; it shares similarities with pumped hydroelectric storage, in use since the 20th century. However, recent advancements in renewable energy systems and the global push toward carbon neutrality have accelerated interest in alternative gravity-based storage technologies. Unlike pumped hydro, gravity batteries can be implemented in diverse terrains and do not require vast amounts of water, making them a versatile solution.
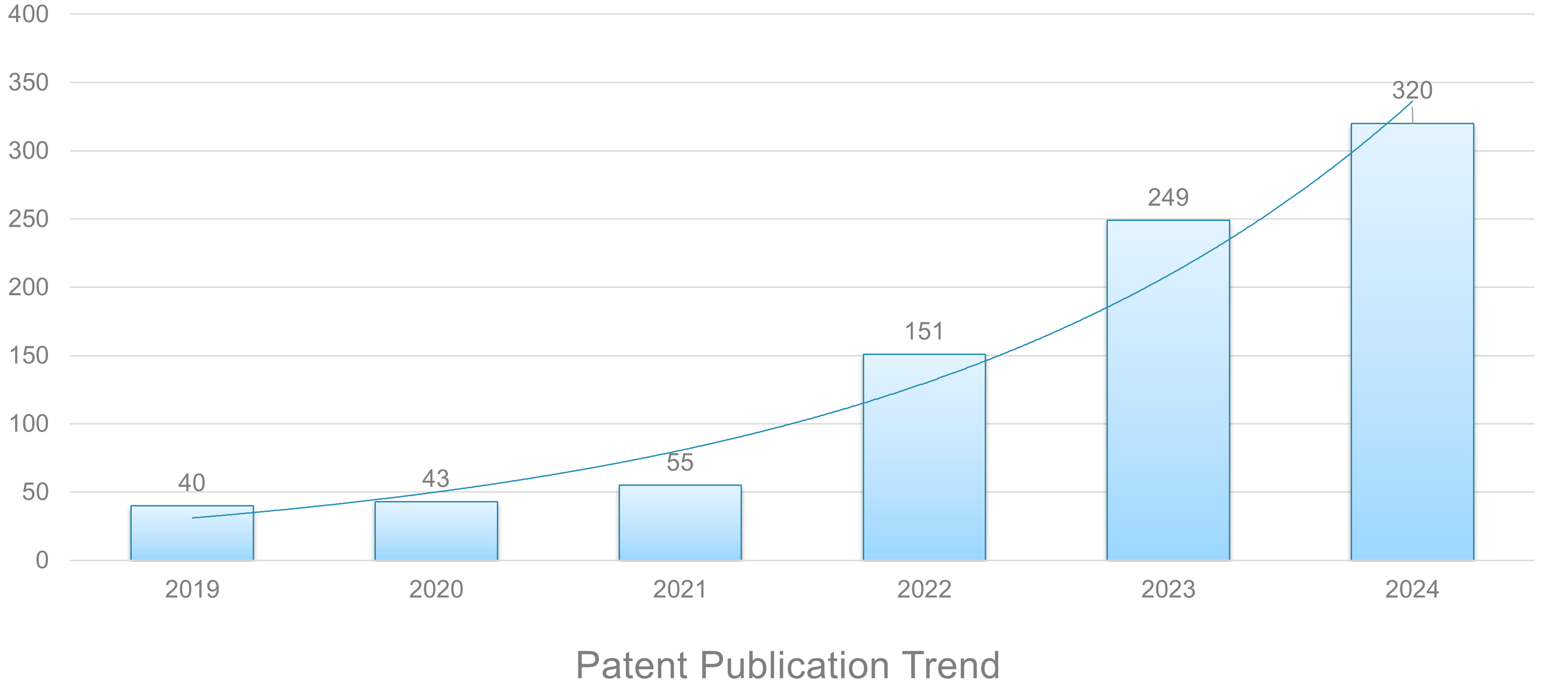
Over the past five years, patenting activity in gravity energy storage has seen a significant surge, with 40 patents published in 2019, rising sharply to 151 in 2022 and 320 in 2024. This rapid growth highlights the increasing focus on gravity energy storage as a viable and competitive technology.
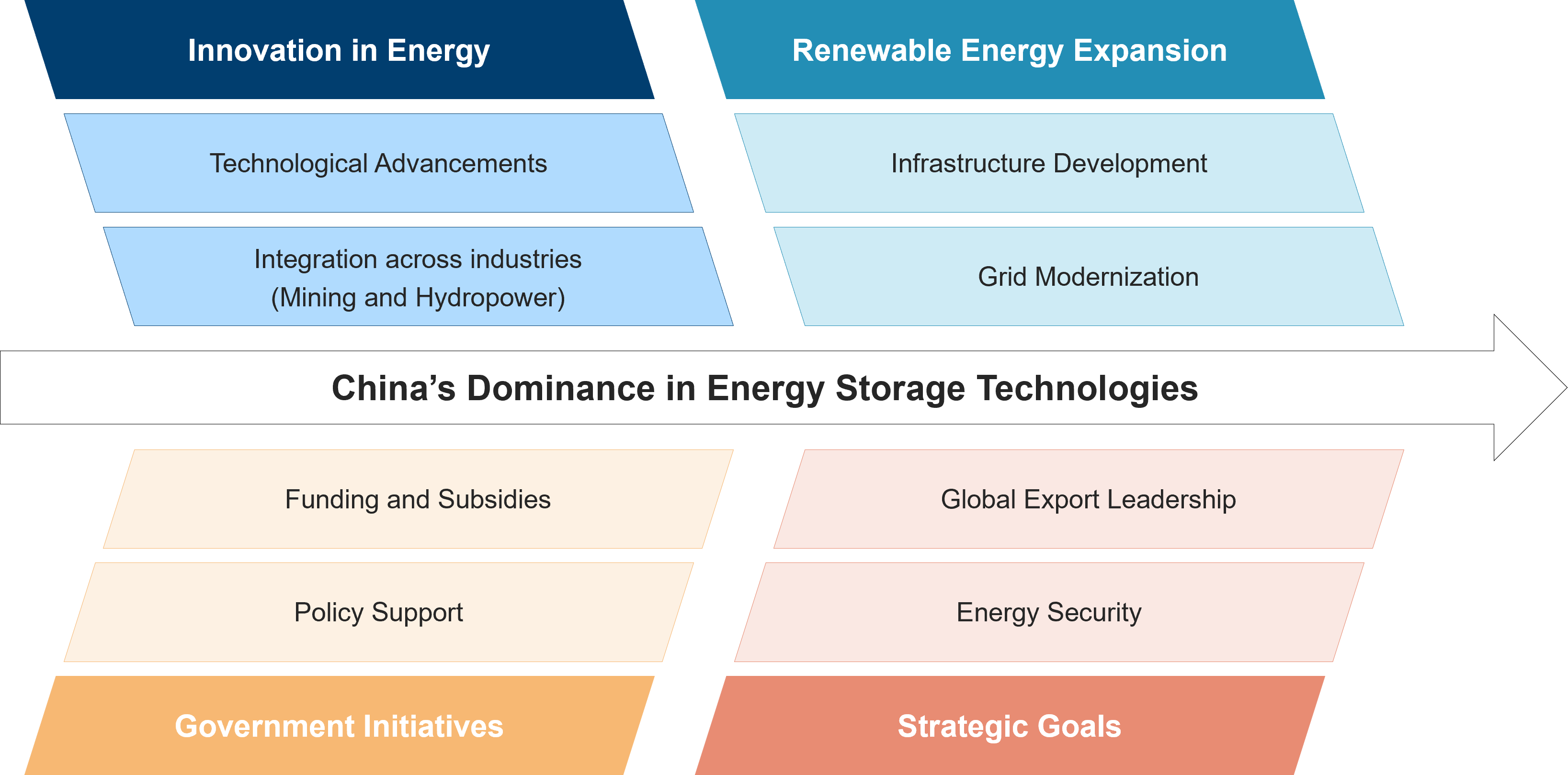
The domain is occupied by Chinese entities, including China Tianying, SGCC - State Grid Corporation of China, State Grid Heilongjiang Electric Power, TPRI, and Guizhou Power Grid. China's dominance can be attributed to its emphasis on innovation in energy, government-backed initiatives, and renewable energy expansion. This dominance underscores China's strategic focus on becoming a leader in advanced energy storage technologies, which aligns with its broader goals of energy security and technological independence, global export leadership and sustainability.
While Chinese entities dominate patenting activity, prominent non-Chinese players like Energy Vault and Gravitricity also hold significant patents. Energy Vault focuses on modular tower-based systems, emphasizing scalability and material efficiency, while Gravitricity specializes in shaft-based systems that leverage abandoned mines.
Patent filings indicate that innovators are focusing on:
- Advanced lifting mechanisms for increased efficiency.
- Integration with smart grids for automated energy management.
- Cost-effective materials and modular designs for scalability.
From Concept to Commercial Reality
The modern iteration of gravity energy storage gained attention in the last decade as engineers sought efficient ways to store surplus renewable energy from wind and solar. Companies like Gravitricity and Energy Vault have been pioneers in transforming this simple concept into scalable commercial systems.
Gravitricity, based in the UK, employs weights suspended in deep mine shafts to store energy, while Energy Vault, a Swiss company, uses massive cranes to stack and unstack concrete blocks around a central tower. These innovations have demonstrated high efficiency, with round-trip efficiencies of up to 85-90%, positioning gravity batteries as serious contenders in the energy storage landscape.
Similarly, Heindl Energy (Germany), developing scalable gravity storage solutions using hydraulic lifting systems and Gravity Power (USA) specializes in shaft-based systems integrated with hydraulic pumps to store and release energy.
Startups in this space are actively securing funding, entering partnerships with utilities, and piloting projects to validate their technologies. Gravitricity’s successful prototype in Scotland and Energy Vault’s multi-million-dollar contracts are clear indicators of the technology’s commercial potential.
Different Design Categories of Gravity Batteries
Gravity batteries can be categorized based on their design and application:
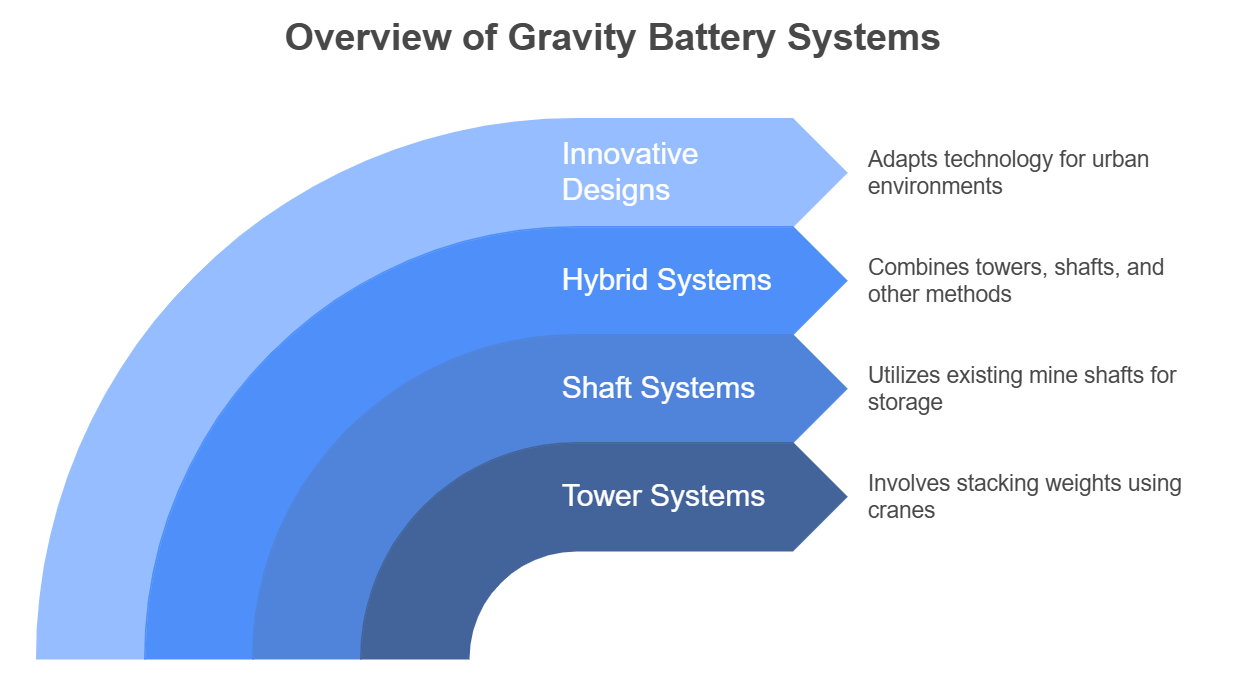
- Tower Systems: These involve stacking weights (e.g., concrete blocks) using cranes, as seen in Energy Vault’s design.
- Shaft Systems: Gravitricity’s model uses vertical underground space in existing mine shafts.
- Hybrid Systems: Some designs incorporate elements of both towers and shafts or integrate additional storage methods like flywheels.
- Innovative Designs: Emerging technologies aim to adapt the concept into urban environments, such as using elevator systems in high-rise buildings to store and release energy.
Parameters Driving Advancements in Gravity Energy Storage
There are several factors prompting innovation in gravity batteries:
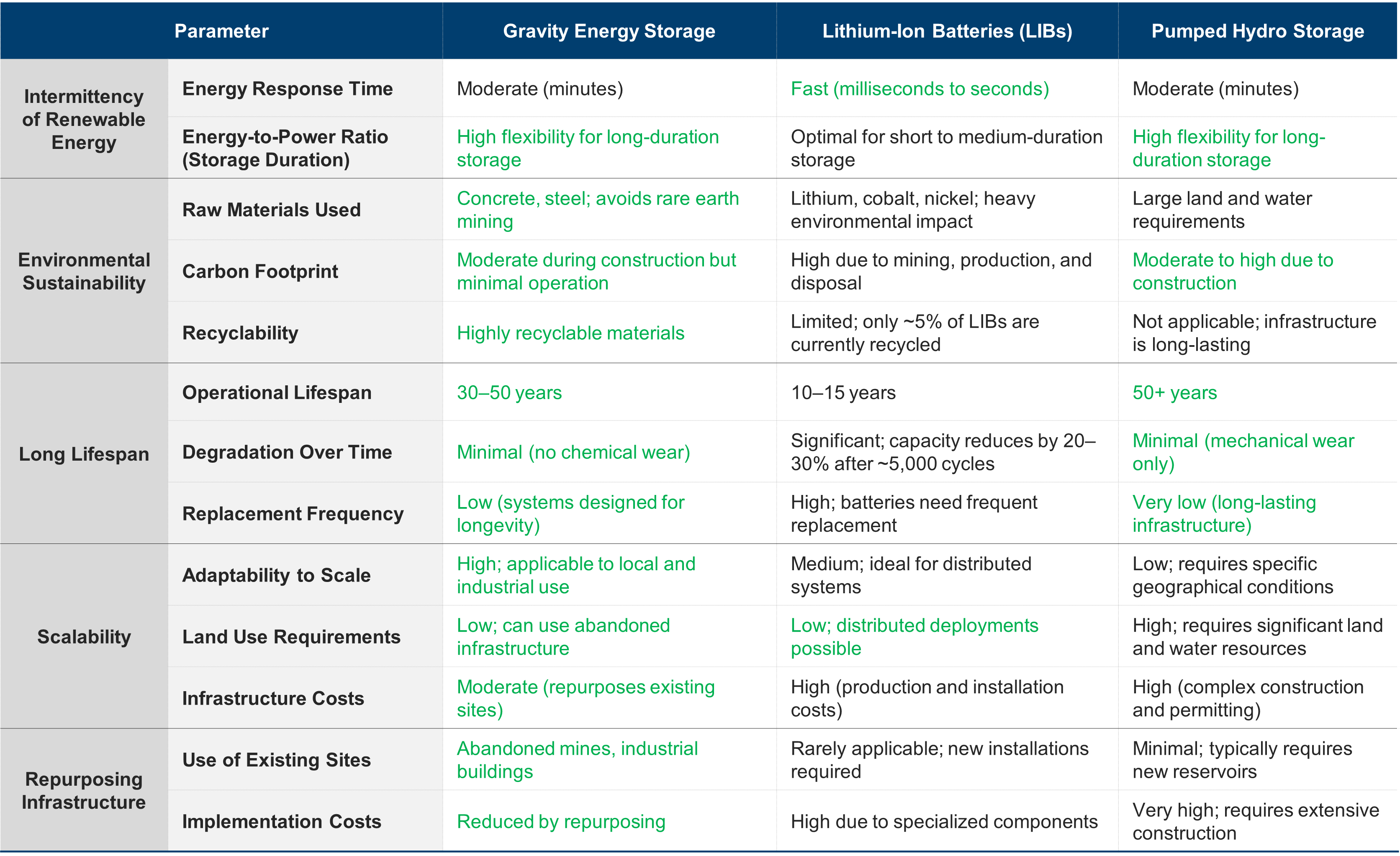
Gravity energy storage demonstrates superior environmental sustainability, longer lifespan, and infrastructure repurposing potential compared to Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). However, it has a slower response time. Pumped hydro storage competes with gravity storage technology in scalability and longevity but faces geographic and land-use limitations. LIBs excel in rapid response and distributed scalability. However, they are environmentally unsustainable and have shorter lifespans.
This analysis highlights gravity batteries as a leading solution for long-duration, sustainable energy storage in renewable grids. Gravity batteries are pivotal for achieving 24/7 energy availability, reducing reliance on LIBs, and complementing other storage technologies. With technological advancements, growing investments, and policy support, gravity storage technology is poised to become the cornerstone of future sustainable energy infrastructure.
