China's Petrochemical Expansion: Reshaping US and Global Trade
Published on 23 Jul, 2024

China's rapid expansion in petrochemical capacity poses a significant challenge to the US, heightening trade tensions. By 2025, China's ethylene capacity is set to reach 50 million metric tonnes (~50–60% increase and its plastics production could hit 120 million tonnes (~30–35% increase over the last 5 years) annually. The resulting oversupply will further depress global prices, threaten the US export volumes to China and other Southeast Asia (SEA) countries and profitability, and reshape global petrochemical market dynamics.
China's accelerated growth in petrochemical capacity positioned it as a major competitor in the global market for petrochemical product exports. This growth aligns with China's economic ambitions, but it creates new challenges and potential trade tensions for the US.
Expansion of China's Petrochemical Industry
China made substantial investments in recent years to boost its petrochemical production. The country's ethylene capacity is anticipated to increase over 50–60% compared to the past five years to reach 50 million metric tonnes by 2025.
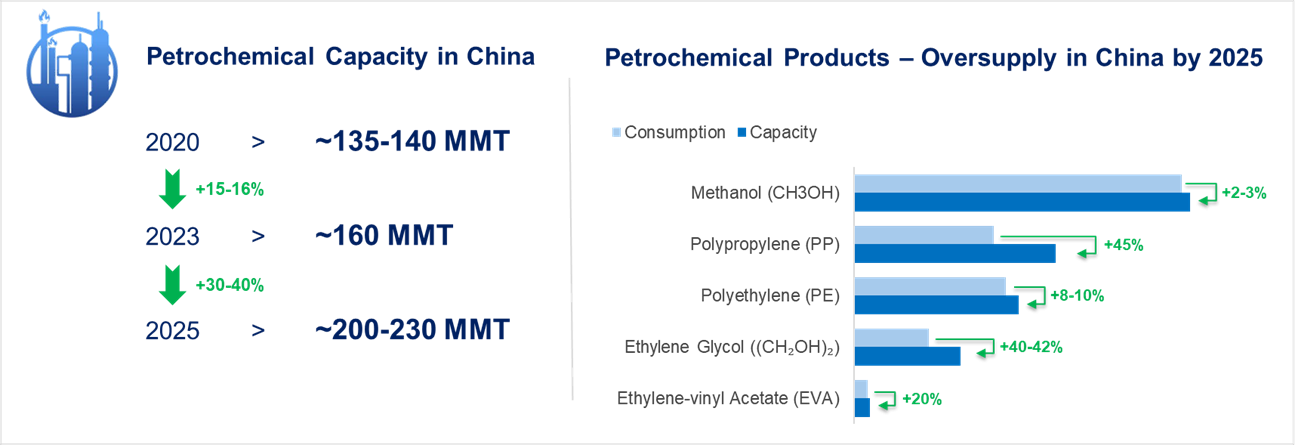
By 2025, China’s production capacity in all major segments (methanol, PP, PE) is expected to exceed consumption levels. This increase is driven by domestic demand and a strategic goal to reduce import dependency.
China's broader industrial policies emphasise technological advancement and increased control over supply chains, underpinning this growth. The increased production capacity caters to domestic consumption and enhances China's position as a key exporter.
Impact on the US Trade Dynamics
China's growing presence in the petrochemical sector plays an increasingly pivotal role in global trade dynamics. Major economies like the US have raised concerns over China's growing influence in the petrochemical market, fearing it may exacerbate existing trade disputes.
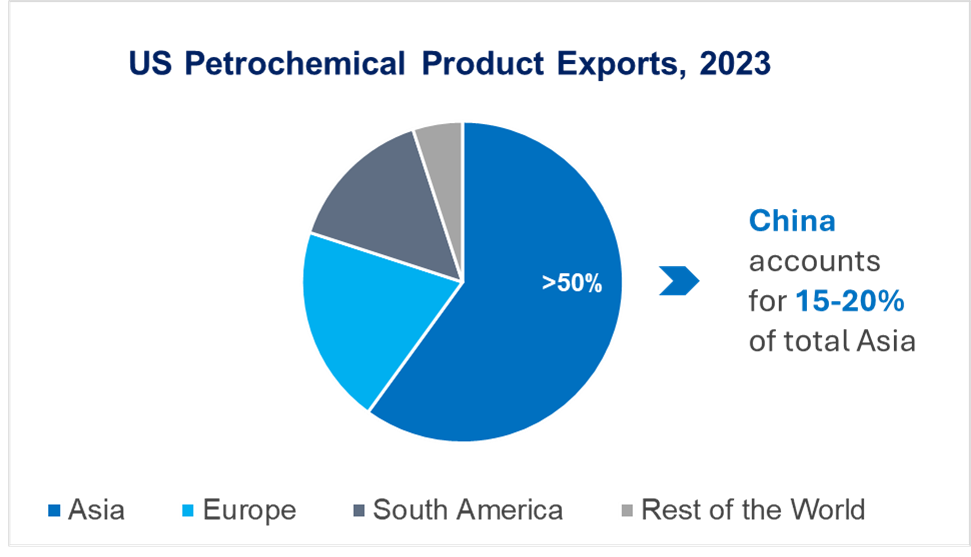
Asia, with China as a significant contributor, holds a substantial share of the US petrochemical product exports. The ongoing expansion of China's production capacity and the prospects of China becoming a net exporter of petrochemical products pose a considerable threat to the US export volumes. This shift could disrupt existing trade balances, reducing market share and profitability for the US petrochemical exporters. Furthermore, the competitive landscape will likely intensify, compelling the US firms to innovate and seek alternative markets to maintain their global standing.
Global Pricing Implications
The substantial increase in Chinese petrochemical production is poised to create an oversupply in the global market, leading to downward pressure on prices. This development could adversely impact producers in other regions. Specifically, the global ethylene market, valued at approximately $160 billion in 2020, might face significant price fluctuations due to this surge in Chinese output. This potential market disruption generates considerable concern among international petrochemical companies and policymakers.
Furthermore, the expected reduction in prices of plastic resins might lead to a decrease in the consumption of post-consumer resin (PCR). As lower prices make virgin resin economically attractive, efforts to boost recycling rates and sustainability in the industry might suffer setbacks. This shift poses a challenge to global initiatives to promote circular economy practices.
Environmental and Regulatory Concerns
China's petrochemical industry faces substantial environmental and regulatory challenges. The sector is a major source of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for about 20% of the nation's industrial emissions. China must navigate stringent environmental regulations at home and abroad as production scales up.
China's target to significantly reduce carbon emissions before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 puts pressure on the petrochemical industry to adopt sustainable practices. Balancing industrial growth with environmental sustainability adds complexity to China's expansion plans.
Conclusion
China's growth in petrochemical capacity represents significant opportunities and formidable challenges. The nation's ability to navigate the complexities of global trade, environmental sustainability and market dynamics will determine the future of its petrochemical industry. Notably, China's petrochemical output is projected to account for 35% of the world's total by 2025, underscoring its influence on global supply chains.
Furthermore, China's potential to drive down global petrochemical prices may lead to significant restructuring within the industry as global players adapt to the new market realities. It is imperative for end-use industries, such as automotive, construction and consumer goods, to consistently monitor and analyse market prices. By doing so, they can strategically establish long- and short-term contracts with resin suppliers. This proactive approach will ensure a competitive edge, effective management of costs and a reliable supply chain.
