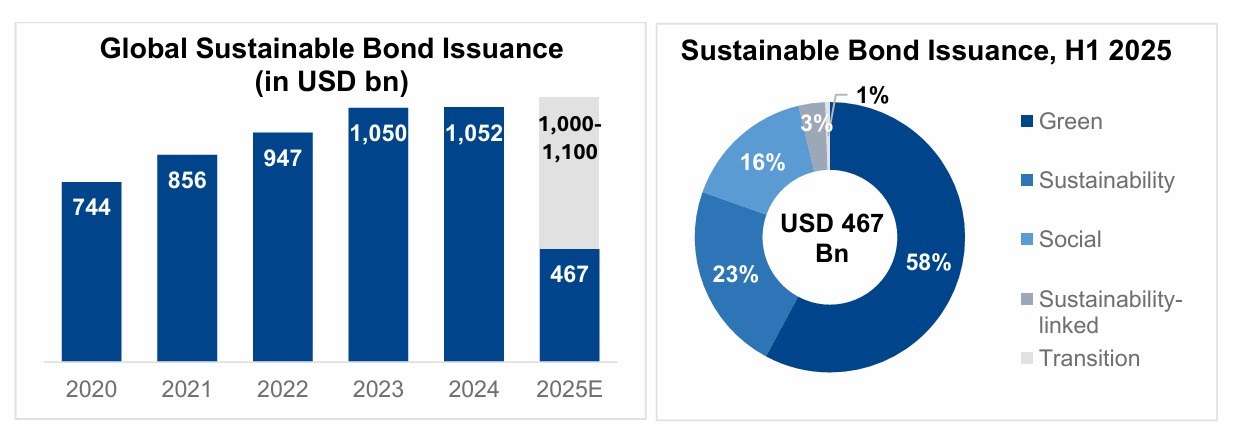
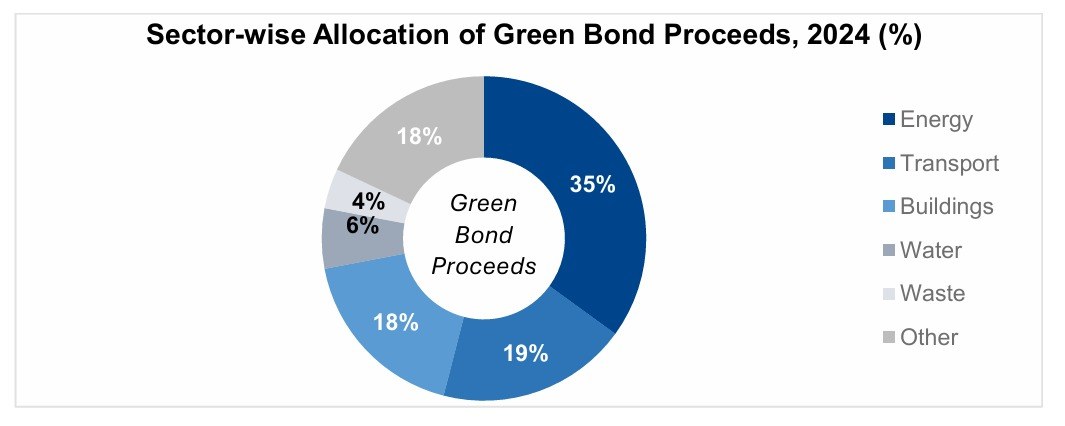
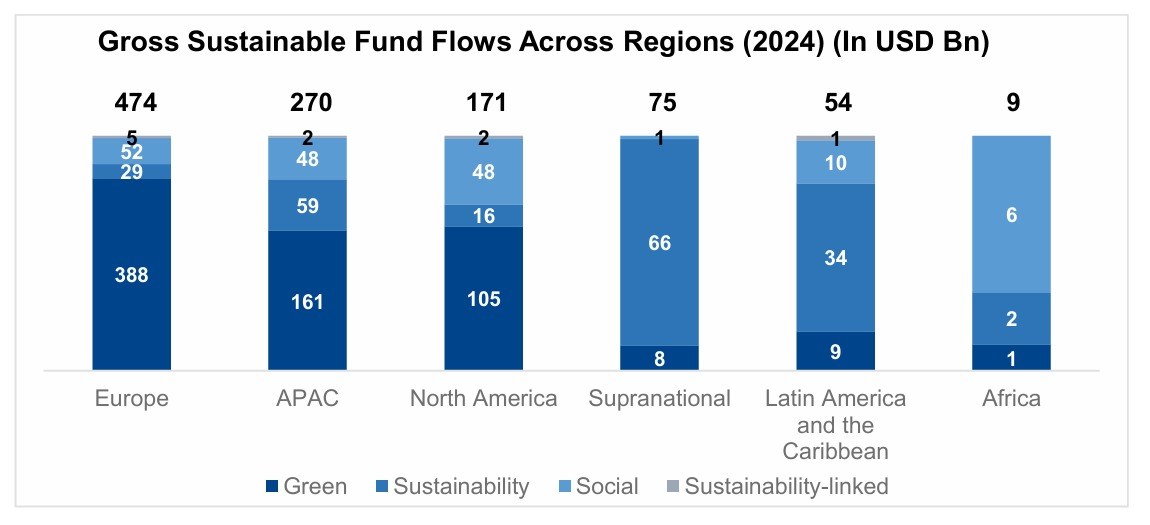
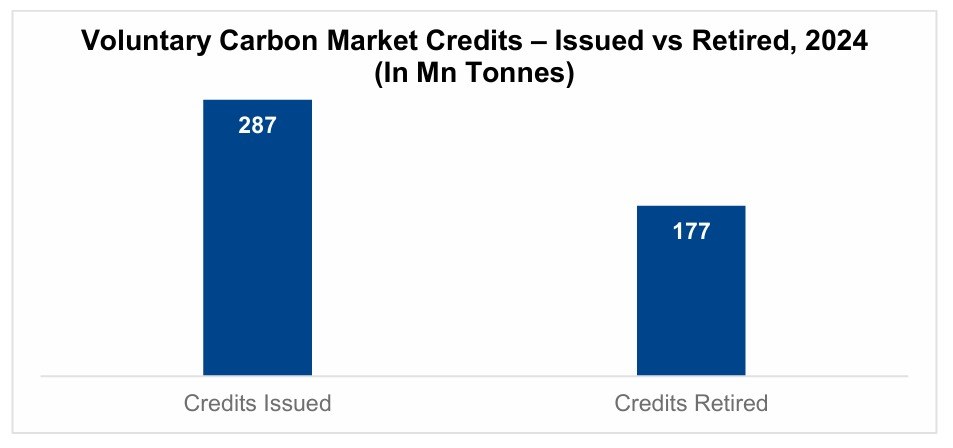
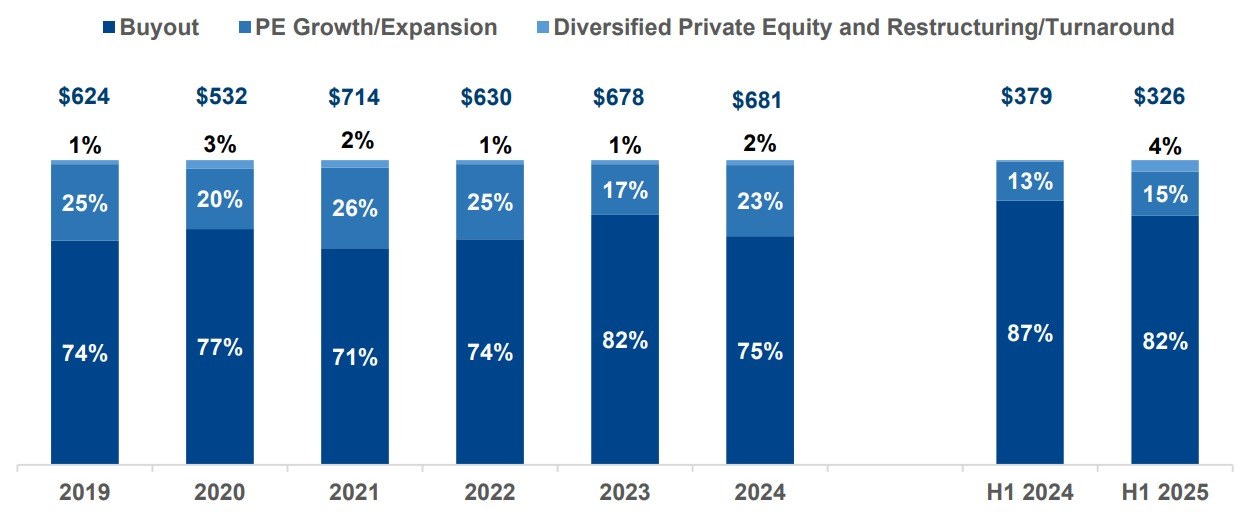
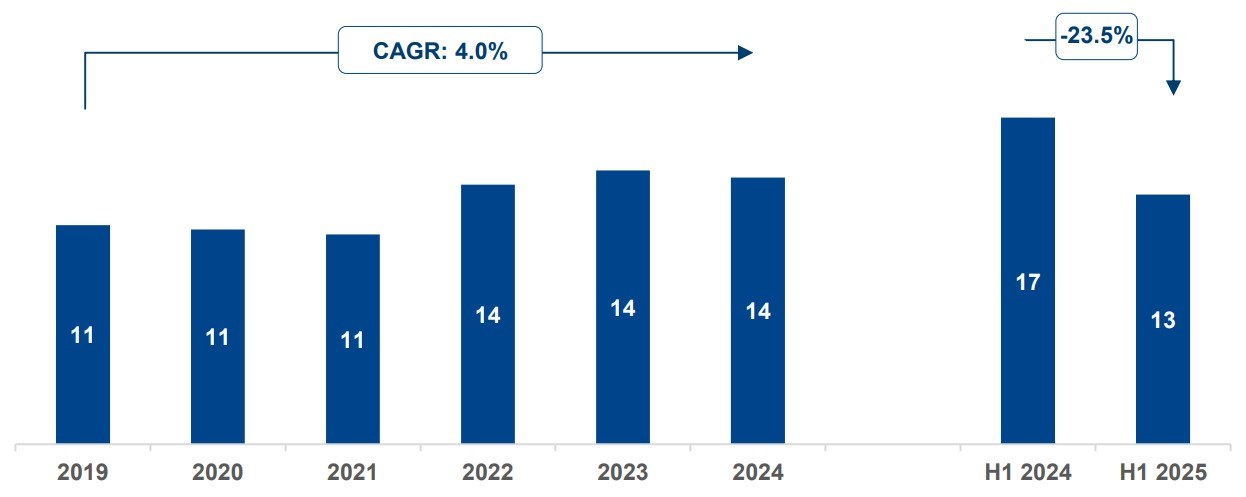
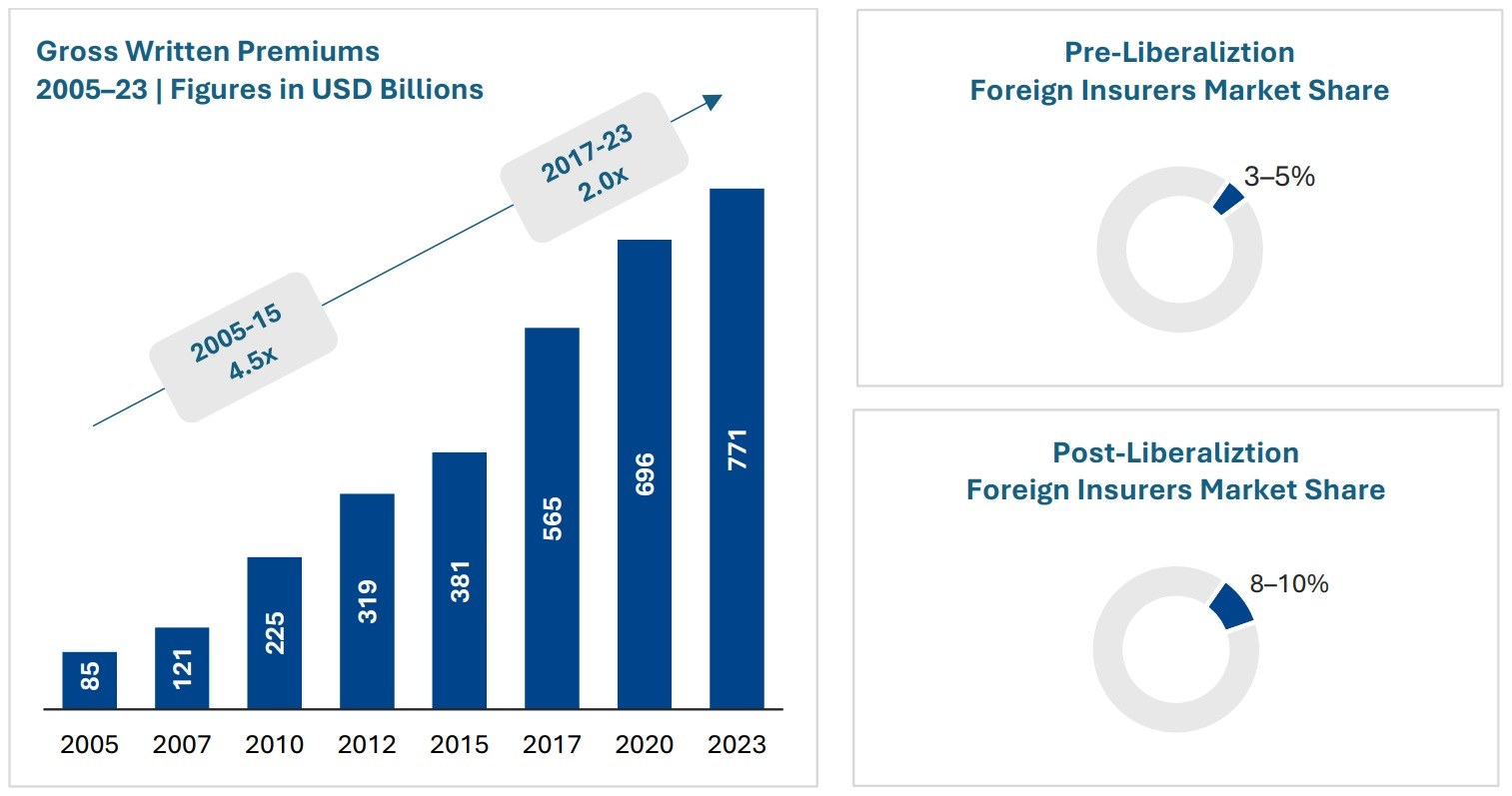
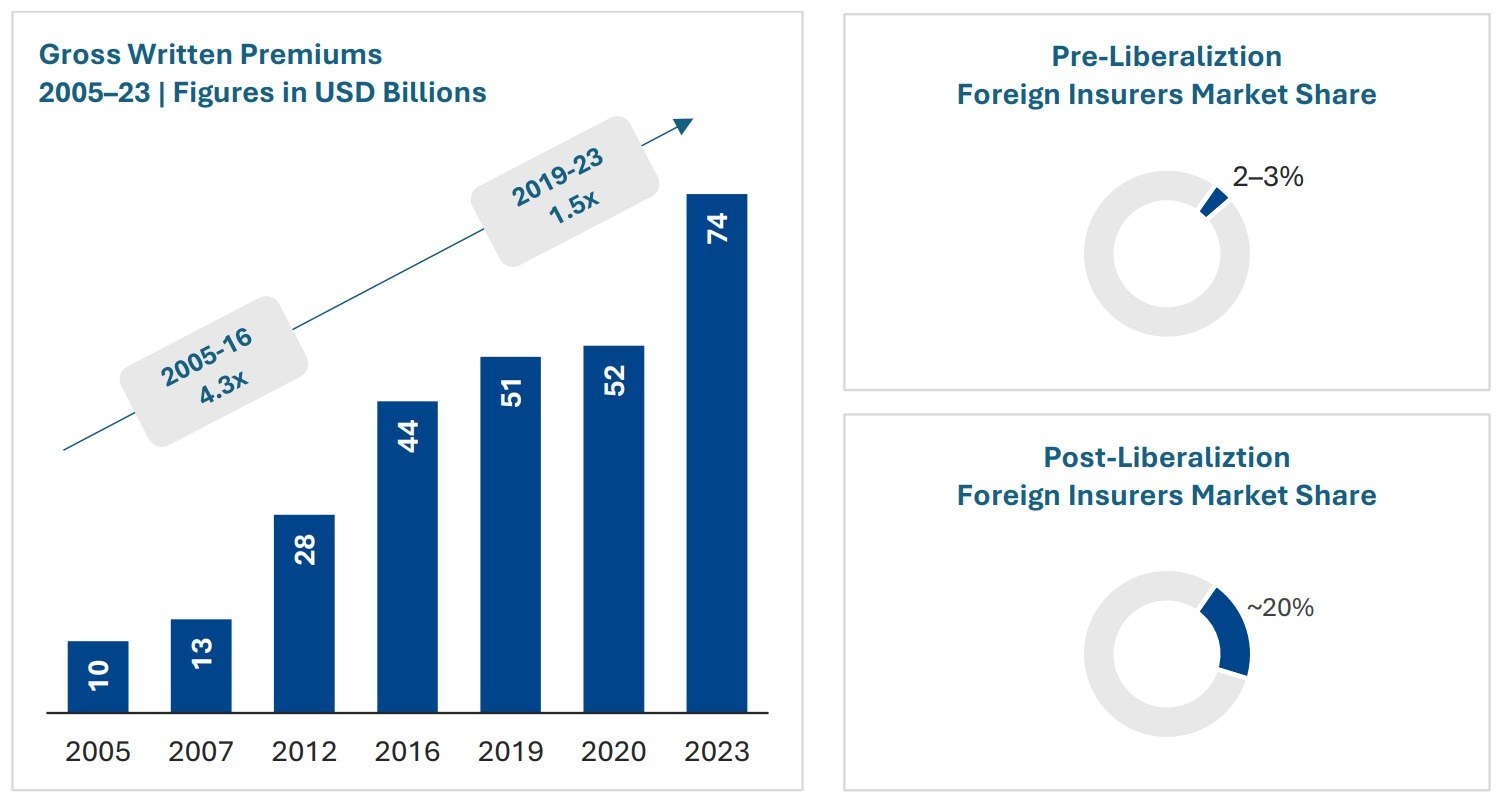
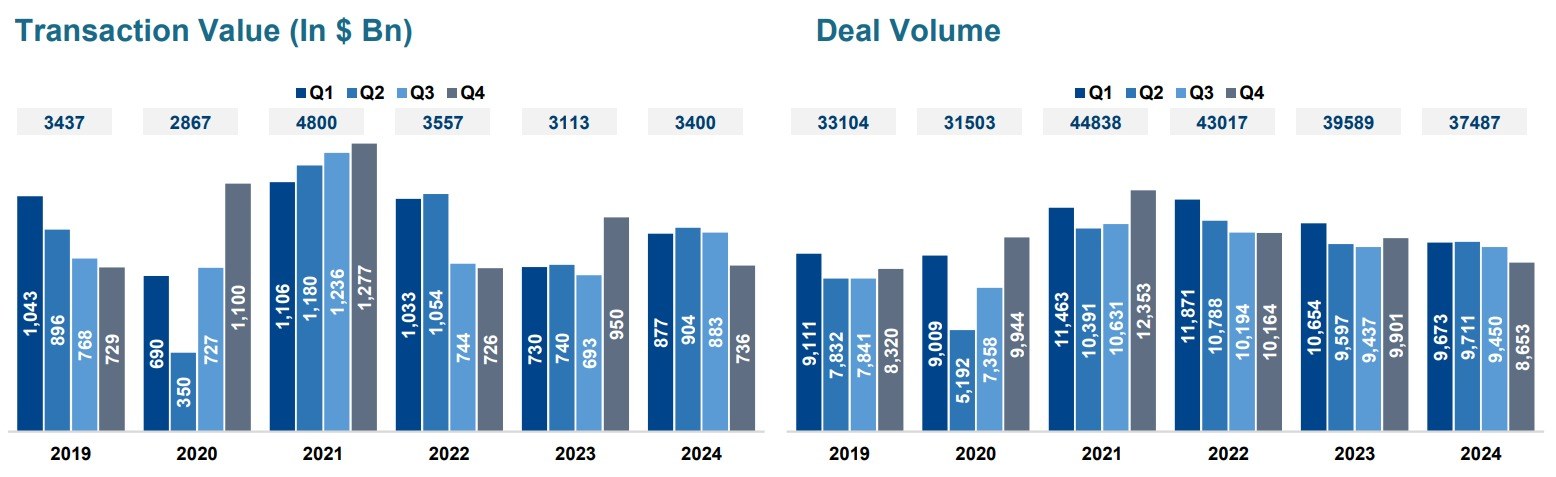
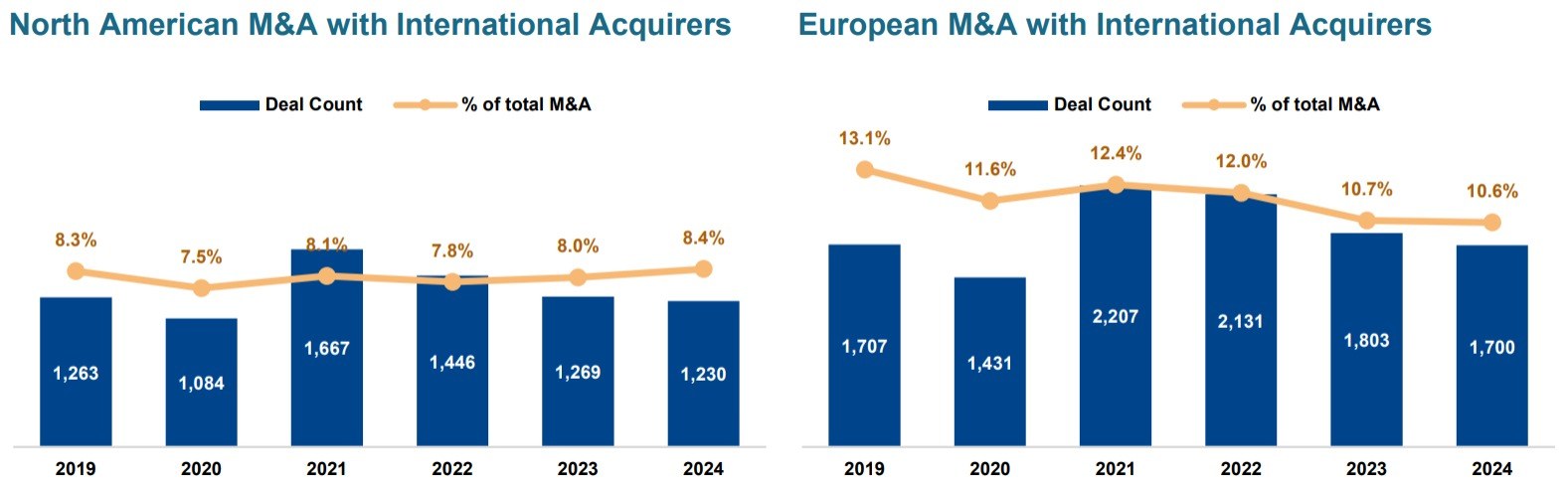
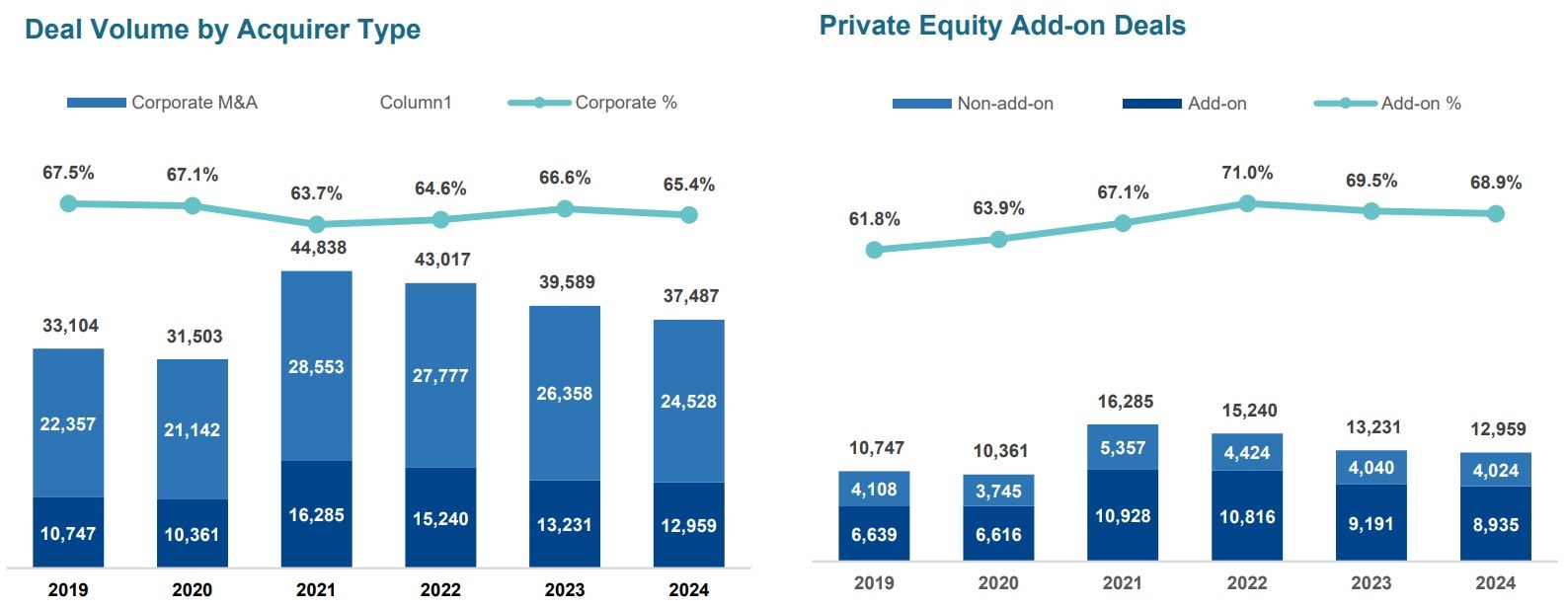
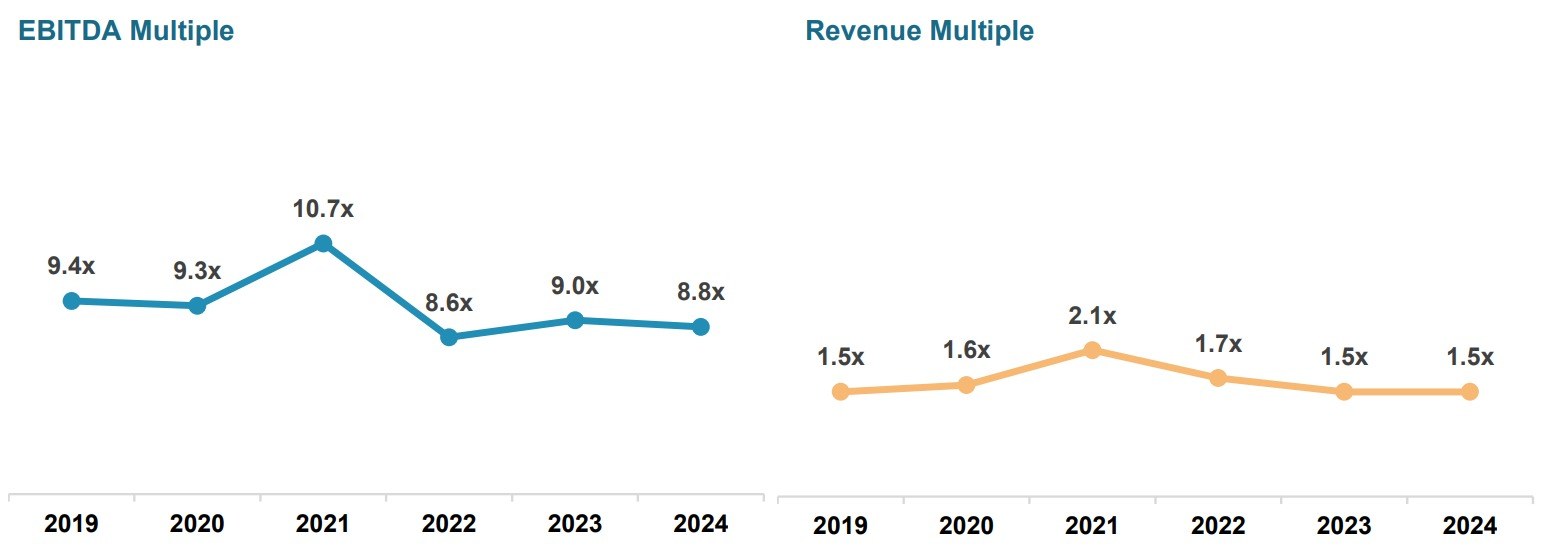
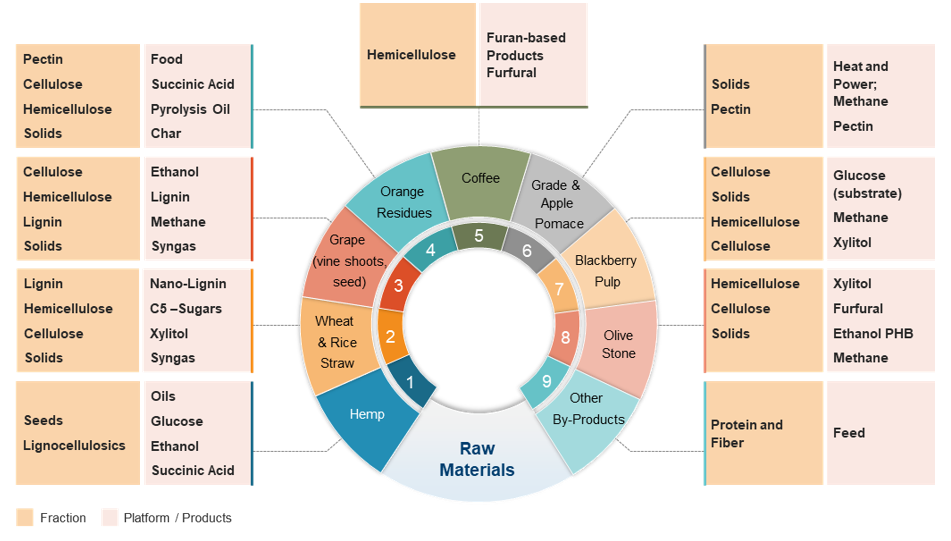
The pandemic brought fore the need for and importance of virtual care. Apart from eliminating distance, virtual health can support in-person care as part of an integrated healthcare strategy. It addresses underserved and under resourced patient populations. By enhancing accessibility, convenience, and the experience of receiving and providing treatment, it has the potential to be advantageous for both patients and doctors. But will it continue to see robust growth post the pandemic?
As technology continues to advance, the healthcare industry is also leveraging the potential of virtual health to increase accessibility to healthcare services. Virtual health, also known as telehealth or telemedicine, refers to the use of digital technologies, such as video conferencing, remote monitoring, mobile health apps and virtual reality, to deliver healthcare services remotely.
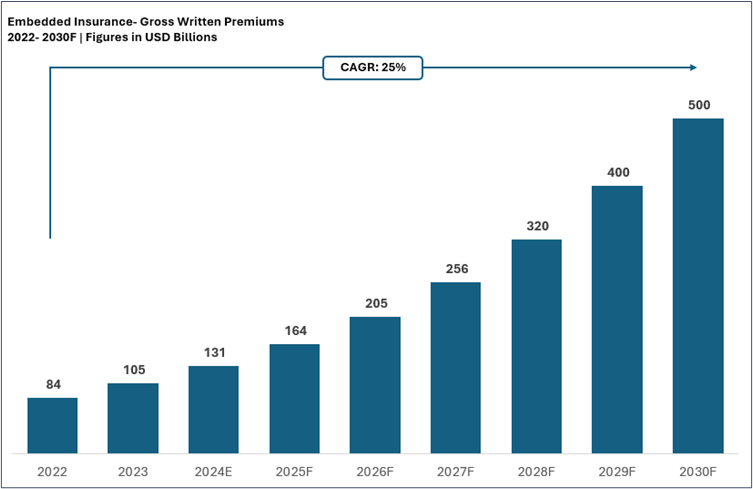
Virtual health has the potential to transform the healthcare industry by improving patient outcomes, increasing access to healthcare services, reducing costs, and enhancing patient experience. The global virtual healthcare market was estimated to be USD2.34 billion in 2021. It is expected to expand at a CAGR of almost 50% to USD17.51 billion during 2022–26.
The virtual healthcare market has accelerated due to factors such as rising healthcare expenses, increased smartphone adoption, and integrated business models. In addition, this market enables resource efficiency and lowers the frequency of in-person consultations for minor medical issues. Its rising emphasis on creating virtual assistance solutions is also creating opportunities for expansion.
Benefits
- Accessibility: The key benefit of virtual health is increased access to healthcare services, particularly in remote and underserved areas. Virtual health enables patients to receive healthcare services from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for travel, thereby allowing healthcare providers to reach a larger patient population.
- Patient outcome: Virtual health can improve patient outcomes as caregivers can conduct remote monitoring and get real-time updates on patient’s health. For instance, remote monitoring devices can track vital signs, such as blood pressure and glucose levels, and alert healthcare providers if there are sudden changes. This can help prevent hospitalizations and critical health issues.
- Patient experience: Virtual health enhances patient experience by providing more convenient and personalized healthcare services. Patients can schedule appointments and receive care at their convenience. There is reduced wait time and access to expert opinion. Healthcare providers can also personalize care based on patient data and preferences, improving patient satisfaction and engagement.
Challenges
Despite the benefits of virtual health, there are still several barriers to adoption. One of the main barriers is the lack of reimbursement for virtual health services. Many healthcare providers are hesitant to adopt virtual health services due to the uncertainty surrounding reimbursement policies, which vary by state and payer. Moreover, there are concerns around the quality of virtual healthcare services and the potential for misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. However, the biggest hurdle seems to be the lack of human touch.
The human touch
Patients often expect a certain level of human interaction and personal connection when seeking medical care. Virtual care may fall short in this aspect, as the absence of physical presence and in-person communication can create a sense of distance between the patient and the clinician. This could lead to a lack of trust and confidence in the clinician, resulting in dissatisfaction with the virtual care experience.
Establishing a good rapport with patients is crucial for this model to be successful. Clinicians and doctors need to be skilled in building relationships with patients virtually, through effective communication, active listening, and empathy.
Another reason for the need for human touch is that workflow and operations are more streamlined in traditional in-person visits that have established processes, with clear guidelines on how to perform physical exams, take vitals, and conduct comprehensive assessments. These processes can be more challenging to replicate in virtual visits, as there may be technical issues or limitations in conducting certain assessments remotely.
Lastly, the clinical considerations for virtual visits are more nuanced, and some clinical decision-making is tougher. Physicians need to rely heavily on the patient's self-reported symptoms and observations, which can be unreliable or incomplete. This could lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, potentially compromising patient outcomes. Healthcare providers can integrate virtual health services with in-person care to provide a more comprehensive and connected healthcare experience. For instance, virtual health services can be used to provide follow-up care after an in-person visit or to provide remote consultations for patients with chronic conditions.
Increasing adoption of virtual care
Virtual care offers many benefits such as increased access to care, improved patient outcomes, and cost savings. While virtual care cannot fully replace in-person care; it can complement it by providing convenient and accessible care options. Yet, its high cost of implementation, and relatively longer period before generating return on investment act as growth barriers.
Providers should carefully consider the benefits and challenges of virtual care and develop strategies to address them while also incorporating the human touch where possible. As technology continues to advance, virtual care is likely to play an increasingly important role in healthcare. Therefore, it is crucial to explore and improve upon its capabilities to provide the best possible care for patients.